What Utility Can You Use to Ensure That an Embedded Port on the Motherboard Is Enabled?
An embedded system is a combination of computer hardware and software designed for a specific office. Embedded systems may also role within a larger system. The systems tin be programmable or have a fixed functionality. Industrial machines, consumer electronics, agricultural and processing industry devices, automobiles, medical equipment, cameras, digital watches, household appliances, airplanes, vending machines and toys, likewise every bit mobile devices, are possible locations for an embedded system.
While embedded systems are computing systems, they can range from having no user interface (UI) -- for example, on devices designed to perform a unmarried chore -- to complex graphical user interfaces (GUIs), such every bit in mobile devices. User interfaces tin can include buttons, LEDs (low-cal-emitting diodes) and touchscreen sensing. Some systems use remote user interfaces besides.
MarketsandMarkets, a business-to-business (B2B) inquiry firm, predicted that the embedded marketplace will be worth $116.2 billion by 2025. Scrap manufacturers for embedded systems include many well-known technology companies, such as Apple, IBM, Intel and Texas Instruments. The expected growth is partially due to the continued investment in artificial intelligence (AI), mobile computing and the need for chips designed for loftier-level processing.
Examples of embedded systems
Embedded systems are used in a wide range of technologies across an array of industries. Some examples include:
- Automobiles. Mod cars unremarkably consist of many computers (sometimes as many as 100), or embedded systems, designed to perform unlike tasks inside the vehicle. Some of these systems perform basic utility functions and others provide entertainment or user-facing functions. Some embedded systems in consumer vehicles include prowl control, fill-in sensors, suspension control, navigation systems and airbag systems.
- Mobile phones. These consist of many embedded systems, including GUI software and hardware, operating systems (OSes), cameras, microphones, and USB (Universal Serial Bus) I/O (input/output) modules.
- Industrial machines. They tin can contain embedded systems, like sensors, and tin be embedded systems themselves. Industrial machines oft have embedded automation systems that perform specific monitoring and control functions.
- Medical equipment. These may comprise embedded systems like sensors and control mechanisms. Medical equipment, such as industrial machines, also must exist very convenient so that human health isn't jeopardized by preventable machine mistakes. This means they'll oft include a more complex Os and GUI designed for an appropriate UI.
How does an embedded organisation work?
Embedded systems always function every bit role of a complete device -- that'south what'due south meant by the term embedded. They are low-toll, low-ability-consuming, small computers that are embedded in other mechanical or electrical systems. By and large, they contain a processor, ability supply, and memory and advice ports. Embedded systems use the communication ports to transmit information between the processor and peripheral devices -- often, other embedded systems -- using a communication protocol. The processor interprets this data with the assistance of minimal software stored on the retention. The software is normally highly specific to the function that the embedded system serves.
The processor may be a microprocessor or microcontroller. Microcontrollers are simply microprocessors with peripheral interfaces and integrated memory included. Microprocessors use separate integrated circuits for memory and peripherals instead of including them on the chip. Both can be used, only microprocessors typically require more support circuitry than microcontrollers considering in that location is less integrated into the microprocessor. The term organisation on a fleck ( SoC ) is often used. SoCs include multiple processors and interfaces on a single chip. They are often used for loftier-volume embedded systems. Some example SoC types are the application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) and the field-programmable gate array (FPGA).
Often, embedded systems are used in real-time operating environments and use a real-time operating system (RTOS) to communicate with the hardware. Near-real-time approaches are suitable at higher levels of chip capability, divers by designers who take increasingly decided the systems are generally fast enough and the tasks tolerant of slight variations in reaction. In these instances, stripped-down versions of the Linux operating system are commonly deployed, although other OSes have been pared down to run on embedded systems, including Embedded Java and Windows IoT (formerly Windows Embedded).
Characteristics of embedded systems
The main characteristic of embedded systems is that they are task-specific.
Additionally, embedded systems tin can include the following characteristics:
- typically, consist of hardware, software and firmware;
- can be embedded in a larger system to perform a specific function, equally they are built for specialized tasks within the system, non diverse tasks;
- can be either microprocessor-based or microcontroller-based -- both are integrated circuits that give the organization compute power;
- are oft used for sensing and real-time computing in internet of things (IoT) devices, which are devices that are cyberspace-connected and do not crave a user to operate;
- can vary in complexity and in function, which affects the type of software, firmware and hardware they use; and
- are frequently required to perform their part under a time constraint to go along the larger system performance properly.
Structure of embedded systems
Embedded systems vary in complexity just, generally, consist of three main elements:
- Hardware. The hardware of embedded systems is based effectually microprocessors and microcontrollers. Microprocessors are very similar to microcontrollers and, typically, refer to a CPU (cardinal processing unit) that is integrated with other basic calculating components such as retentivity fries and digital signal processors (DSPs). Microcontrollers have those components congenital into one fleck.
- Software and firmware. Software for embedded systems tin can vary in complexity. However, industrial-grade microcontrollers and embedded IoT systems usually run very simple software that requires little memory.
- Real-time operating organization. These are not ever included in embedded systems, especially smaller-scale systems. RTOSes define how the system works by supervising the software and setting rules during program execution.
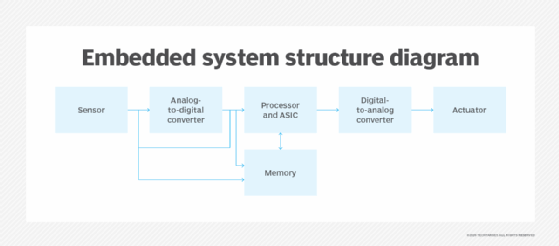
In terms of hardware, a basic embedded system would consist of the following elements:
- Sensors catechumen physical sense information into an electrical signal.
- Analog-to-digital (A-D) converters change an analog electrical signal into a digital one.
- Processors process digital signals and store them in memory.
- Digital-to-analog (D-A) converters change the digital information from the processor into analog data.
- Actuators compare actual output to memory-stored output and choose the correct one.
The sensor reads external inputs, the converters brand that input readable to the processor, and the processor turns that information into useful output for the embedded system.
Types of embedded systems
There are a few basic embedded system types, which differ in their functional requirements. They are:
- Mobile embedded systems are small-sized systems that are designed to be portable. Digital cameras are an example of this.
- Networked embedded systems are connected to a network to provide output to other systems. Examples include home security systems and point of sale (POS) systems.
- Standalone embedded systems are not reliant on a host system. Like any embedded organization, they perform a specialized task. Withal, they practise not necessarily belong to a host system, unlike other embedded systems. A calculator or MP3 histrion is an instance of this.
- Existent-fourth dimension embedded systems give the required output in a divers fourth dimension interval. They are ofttimes used in medical, industrial and military sectors because they are responsible for time-critical tasks. A traffic control organisation is an example of this.
Embedded systems can likewise be categorized by their functioning requirements:
- Small embedded systems oftentimes use no more than than an 8-scrap microcontroller.
- Medium-scale embedded systems use a larger microcontroller (xvi-32 bit) and frequently link microcontrollers together.
- Sophisticated-calibration embedded systems frequently employ several algorithms that result in software and hardware complexities and may require more complex software, a configurable processor and/or a programmable logic array.
There are several common embedded organisation software architectures, which become necessary as embedded systems grow and go more circuitous in scale. These include:
- Unproblematic control loops call subroutines, which manage a specific part of the hardware or embedded programming.
- Interrupt controlled systems have two loops: a main one and a secondary one. Interruptions in the loops trigger tasks.
- Cooperative multitasking is essentially a elementary command loop located in an application programming interface (API).
- Preemptive multitasking or multithreading is often used with an RTOS and features synchronization and chore switching strategies.
Very big-calibration integration, or VLSI, is a term that describes the complexity of an integrated circuit (IC). VLSI is the process of embedding hundreds of thousands of transistors into a chip, whereas LSI (large-scale integration) microchips contain thousands of transistors, MSI (medium-calibration integration) contains hundreds of transistors, and SSI (small integration) contains tens of transistors. ULSI, or ultra-large-scale integration, refers to placing millions of transistors on a chip.
VLSI circuits are common features of embedded systems. Many ICs in embedded systems are VLSIs, and the use of the VLSI acronym has largely fallen out of favor.
Debugging embedded systems
One area where embedded systems role means with the operating systems and development environments of other larger-scale computers is in the surface area of debugging. Usually, developers working with desktop estimator environments have systems that can run both the code being adult and split debugger applications that can monitor the embedded arrangement programmers generally cannot, however.
Some programming languages run on microcontrollers with plenty efficiency that rudimentary interactive debugging is available directly on the bit. Additionally, processors ofttimes have CPU debuggers that can be controlled -- and, thus, control program execution -- via a JTAG or similar debugging port.
In many instances, yet, programmers need tools that attach a separate debugging organization to the target system via a series or other port. In this scenario, the programmer tin can see the source code on the screen of a general-purpose estimator, just as would be the case in the debugging of software on a desktop estimator. A dissever, frequently used approach is to run software on a PC that emulates the physical chip in software. This is essentially making information technology possible to debug the functioning of the software as if information technology were running on an bodily physical scrap.
Broadly speaking, embedded systems take received more than attention to testing and debugging considering a great number of devices using embedded controls are designed for use, particularly in situations where safety and reliability are top priorities.
History of embedded systems
Embedded systems date back to the 1960s. Charles Stark Draper adult an integrated excursion in 1961 to reduce the size and weight of the Apollo Guidance Computer, the digital system installed on the Apollo Command Module and Lunar Module. The start figurer to utilize ICs, information technology helped astronauts collect real-time flight information.
In 1965, Autonetics, now a part of Boeing, adult the D-17B, the computer used in the Minuteman I missile guidance system. It is widely recognized as the first mass-produced embedded system. When the Minuteman II went into production in 1966, the D-17B was replaced with the NS-17 missile guidance system, known for its high-book apply of integrated circuits. In 1968, the kickoff embedded organisation for a vehicle was released; the Volkswagen 1600 used a microprocessor to control its electronic fuel injection system.
By the tardily 1960s and early 1970s, the toll of integrated circuits dropped and usage surged. The get-go microcontroller was developed by Texas Instruments in 1971. The TMS1000 series, which became commercially available in 1974, contained a 4-fleck processor, read-only memory (ROM) and random-access memory (RAM), and information technology price around $2 apiece in majority orders.
Also, in 1971, Intel released what is widely recognized as the start commercially available processor, the 4004. The four-bit microprocessor was designed for apply in calculators and small electronics, though it required eternal memory and back up chips. The 8-bit Intel 8008, released in 1972, had sixteen KB of memory; the Intel 8080 followed in 1974 with 64 KB of memory. The 8080's successor, the x86 series, was released in 1978 and is still largely in apply today.
In 1987, the get-go embedded operating system, the real-time VxWorks, was released past Wind River, followed by Microsoft's Windows Embedded CE in 1996. By the belatedly 1990s, the outset embedded Linux products began to appear. Today, Linux is used in almost all embedded devices.
Embedded system trends
While some embedded systems can exist relatively unproblematic, they are becoming more circuitous, and more than and more of them are now able to either supplant human decision-making or offer capabilities across what a man could provide. For instance, some aviation systems, including those used in drones, are able to integrate sensor data and act upon that information faster than a human could, permitting new kinds of operating features.
The embedded organisation is expected to go on growing rapidly, driven in big part by the net of things. Expanding IoT applications, such equally wearables, drones, smart homes, smart buildings, video surveillance, 3D printers and smart transportation, are expected to fuel embedded arrangement growth.
This was concluding updated in December 2020
Continue Reading About embedded system
- Mobile embedded applications: Seven testing challenges
- Embedded hypervisor employ cases and benefits explained
- What strategies are all-time to ensure a secure embedded system?
- Embedded organisation applications nowadays new challenges
- Embedded systems security a growing concern amidst rising of IoT
Dig Deeper on IoT Manufacture and Vertical Markets
-

smart card
-

embedded operating arrangement
-

Machine learning on microcontrollers enables AI
-

integrated circuit (IC)
Source: https://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/definition/embedded-system



0 Response to "What Utility Can You Use to Ensure That an Embedded Port on the Motherboard Is Enabled?"
Post a Comment